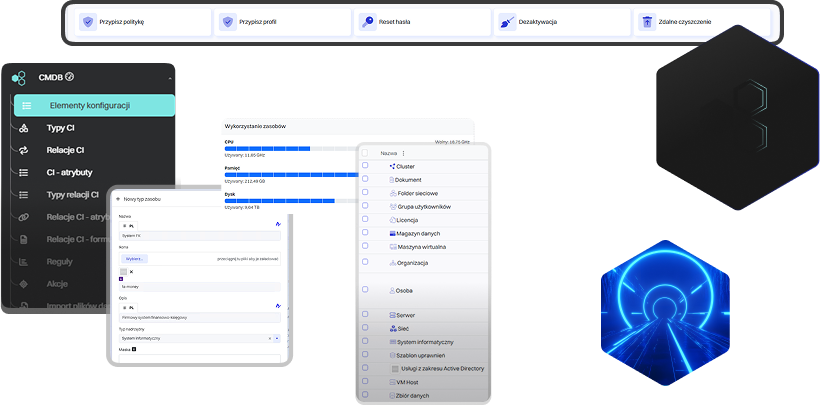
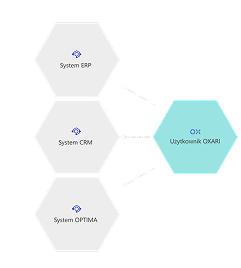
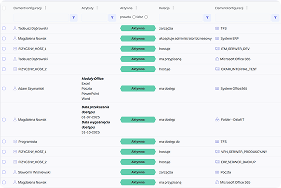
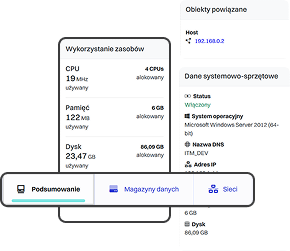
A CMDB is a collection of information about the components that make up an IT infrastructure. The primary object in the database is a configuration item (CI). Selected CIs in the CMDB are linked to each other through relationships (using the appropriate attributes), forming specific services supported by the organization’s IT department (e.g., Email, ERP System). The most common types of configuration items (asset management) include computer hardware, servers, switches, routers, and storage arrays. Configuration items also include all kinds of software – from operating systems and databases to specific applications. Components of a CMDB also include the organization’s employees and the roles and permissions closely associated with them.
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a key element in ITSM processes, providing a central knowledge repository for all components of the IT infrastructure and their interdependencies. With a CMDB, an organization gains full visibility into its assets and the ability to track changes over time.
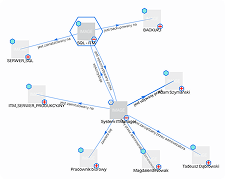
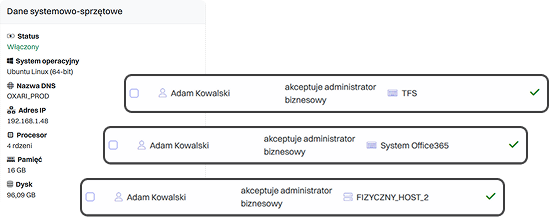
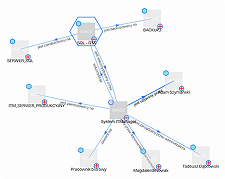
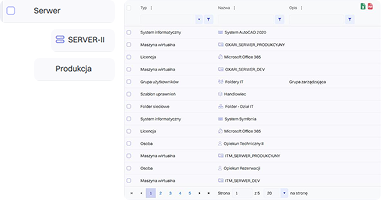
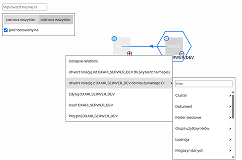
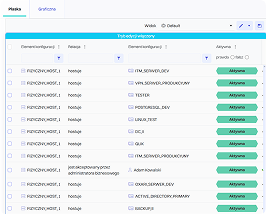
In practice, this means that every configuration item (CI) – a server, database, application, or network device—is described by a set of attributes such as owner, location, serial number, or related business services. The relationships between CIs make it possible to create dependency maps that help understand how the failure of one component may affect other parts of the infrastructure or critical business processes.
Thanks to a CMDB, the IT department can:
- Quickly diagnose problems—knowing which systems are linked to an incident
- Plan changes more effectively—assessing the risk and scope of modifications
- Ensure regulatory compliance—maintaining a complete configuration history
- Optimize costs—eliminating unused or duplicated assets
Combined with processes such as Change Management, Incident Management, and Asset Management, the CMDB becomes the foundation of proactive IT management and a cornerstone for ITIL- or DevOps-based initiatives.